Solar Power Forecasting using LSTM
Live Interaction 
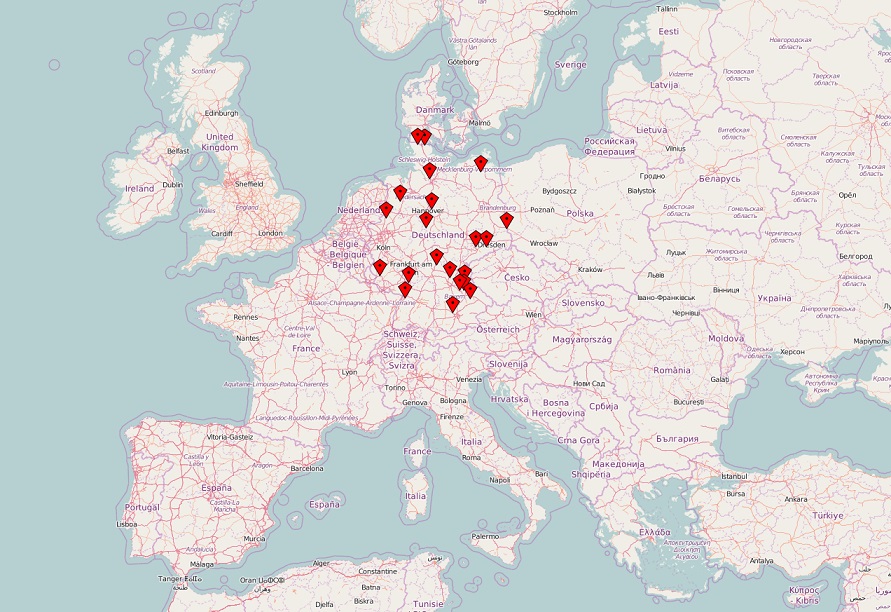
German Solar Farm locations :
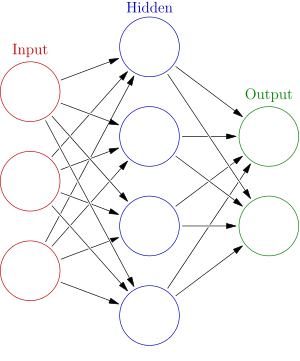
Deciption of a Neural Network :
PROBLEM STATEMENT: -
Power forecasting of renewable energy power plants is a very active research field, as reliable information about the future power generation allow for a safe operation of the power grid and helps to minimize the operational costs of these energy sources. Deep Learning algorithms have shown to be very powerful in forecasting tasks, such as economic time series or speech recognition. Up to now, Deep Learning algorithms have only been applied sparsely for forecasting renewable energy power plants. By using different Deep Learning and Artificial Neural Network Algorithms, such as LSTM, we introduce these powerful algorithms in the field of renewable energy power forecasting. Our motive is to show the forecast strength of these algorithms compared to a standard MLP and a physical forecasting model in the forecasting the energy output of 21 solar power plants and compare our results with results obtained from Artificial Neural Networks as well as other reference models such as physical models.
DATASET EXPLAINED:
The GermanSolarFarm data set contains 21 photovoltaic facilities in Germany. Their installed nominal power ranges between 100kW and 8500kW. The PV facilities range from PV panels installed on rooftops to fully fledged solar farms. They are distributed throughout Germany as shown in the attached image. For each facility historical NWP data and the produced power in a three-hour resolution for 990 days are available. All-time series in the data set, except the measured power output, are normalized between 0 and 1 using the min max normalization. The target variable, the measured power output, is normalized using the nominal output capacity of the corresponding PV facility. Therefore, allow the comparison of the forecasting performance without taking the size of the PV facilities into account.
TECHNIQUES AND ALGORITHMS USED:
PCA (Principle Component Analysis):
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is a dimension-reduction tool that can be used to reduce a large set of variables to a small set that still contains most of the information in the large set. The first principal component accounts for as much of the variability in the data as possible, and each succeeding component accounts for as much of the remaining variability as possible.
METHOD:
1) Calculate the covariance matrix
2) Calculate the eigenvectors and eigenvalues of the covariance matrix Since the covariance matrix is square, we can calculate the eigenvectors and eigenvalues for this matrix. These are rather important, as they tell us useful information about our data. By this process of taking the eigenvectors of the covariance matrix, we have been able to extract lines that characterize the data.
3) Form a feature vector, which is just a fancy name for a matrix of vectors. This is constructed by taking the eigenvectors that you want to keep from the list of Eigen vectors and forming a matrix with these eigenvectors in the columns.
𝐹𝑒𝑎𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑒𝑉𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 = (𝑒𝑖𝑔1 𝑒𝑖𝑔2 𝑒𝑖𝑔3 … … . . 𝑒𝑖𝑔𝑁)
4) Deriving the new data set
𝐹𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙𝐷𝑎𝑡𝑎 = 𝑅𝑜𝑤𝐹𝑒𝑎𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑒𝑉𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 𝑋 𝑅𝑜𝑤𝐷𝑎𝑡𝑎𝐴𝑑𝑗𝑢𝑠𝑡
ANN (Artificial Neural Network): -
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) or connection systems are computing systems vaguely inspired by the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains. Such systems “learn” (i.e. progressively improve performance on) tasks by considering examples, generally without task-specific programming. An ANN is based on a collection of connected units or nodes called artificial neurons (a simplified version of biological neurons in an animal brain). Each connection (a simplified version of a synapse) between artificial neurons can transmit a signal from one to another. The artificial neuron that receives the signal can process it and then signal artificial neurons connected to it.
Steps:
- The Principal Component Analysis yields us 10 principal components accounting for 85.63% of variance
- Now the input is 10 units so we have to choose at least 10 Neurons for the 1st layer of the hidden network.
- The purpose of ANN is to account for variable in a nonlinear manner hence denser the hidden layer better the output
- We choose sigmoid function as activation function because it is smooth and nonlinear increase and it is used to regulate the output in accordance.
- We choose mean squared error as loss function.
- Finally we run the above neural network for 500 epochs getting an accuracy of 40.1%. PCA Data Preprocessing ANN Training and Testing
Libraries Used:
Scikit-Learn:
Scikit-learn (formerly scikits.learn) is a free software machine learning library for the Python programming language It features various classification, regression and clustering algorithms including support vector machines, random forests, gradient boosting, k-means and DBSCAN, and is designed to interoperate with the Python numerical and scientific libraries NumPy and SciPy.
<br> ##### Keras:
Keras is a high-level neural networks API, written in Python and capable of running on top of TensorFlow, CNTK, or Theano. It was developed with a focus on enabling fast experimentation.
<br> ##### Pandas:
Pandas is an open source, BSD-licensed library providing high-performance, easy-to- use data structures and data analysis tools for the Python programming language.
<br> ##### Matplotlib:
Matplotlib is a Python 2D plotting library which produces publication quality figures in a variety of hardcopy formats and interactive environments across platforms. Matplotlib can be used in Python scripts, the Python and iPython shells, the Jupyter notebook, web application servers, and four graphical user interface toolkits.
<br> ##### PVlib:
PVLIB Python is a community supported tool that provides a set of functions and classes for simulating the performance of photovoltaic energy systems.
<br> ##### Itertools:
Itertools is a module for the Python language which contains high level functional constructs for working with iterable objects and generators. Itertools is a module for the Python language which contains high level functional constructs for working with iterable objects and generators.
<br> ##### Numpy:
NumPy is a library for the Python programming language, adding support for large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices, along with a large collection of high-level, mathematical functions to operate on these arrays.
RESULTS:
RMSE(𝑥′ , 𝑥)= 1 𝑁 . ∑ (𝑥′ 𝑛 − 𝑥 𝑛)2𝑁 𝑛=1
RMSE: 21.4%
Accuracy: 40.7%
CONCLUSION:
The results showed that the ANN models have a lower RMSE than the physical reference model. This shows the feature extraction capability of these models, which enables a good solar power forecast. The P-PVFM overestimates the power output of the solar facilities and the DNN models slightly underestimate the power output. In an application of these models, it needs to be taken into account if an overestimation or an underestimation is preferred. If a Rectified Linear Unit (Relu) as activation function for the neural network is chosen over a tanh activation function, it is possible to eliminate erroneous prediction data. This effect of the tanh activation function is especially prominent during the winter when there is snowfall. The reason for this might be that the network learned that during snowfall, the energy output is reduced and tries to reduce the prediction even further. The Relu can resolve this issue as it only propagates a value if the inputs are positive. The performance achieved by ANN architectures in forecasting of solar power might also be transferred to other regenerative energy sources, e.g., forecasting of wind power output.